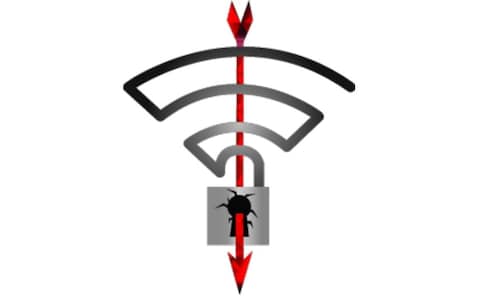
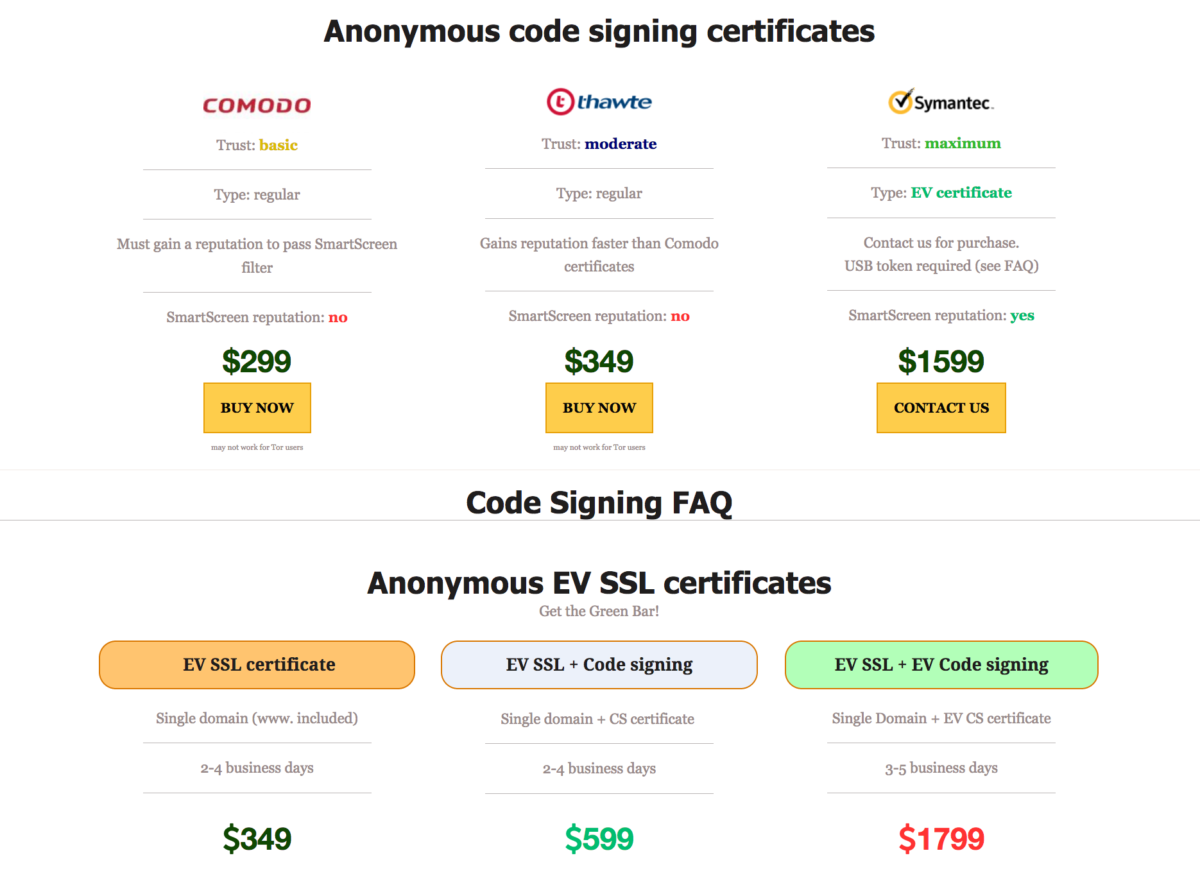
The previous trend of using stolen certificates to digitally sign malware (to circumvent OS’s requirements for valid digital signatures om files to install SW) has been overtaken by black hats issuing counterfeit certificates pretending to be the institution the certificates are issued to. Social engineering to the next leve is one way of looking at this. Recorded Future has an analysis of the current market place, with a tracking of the 3 largest dark web merchants and their volumes over the last 5 years. Also a breakdown of the current offerings available. Note that the high-end certs are Symantec Certs, the CA that got phased ut by the browser vendors after numerous issues, so the hope is that this will remove the EV certificates from this kind of use.
Tag: Hacking
[Updated] More Apple iOS source code leaks (iBoot)
Yet more Apple source code has been leaked, this time around the iBoot elements of IOS. Although from an older build of IOS (9x) it should be close to the current implementation. Initially leaked on Reddit by a user named apple_internals and subsequently removed, now posted in Github for maximum availability. An good article on Motherboard does some initial analysis and impact analysis. It’s a shame jailbreaking has gone out of Vogue, this will make it a lot simpler to do.
[Update] Apple has released the following statement” Old source code from three years ago appears to have been leaked, but by design the security of our products doesn’t depend on the secrecy of our source code. There are many layers of hardware and software protections built in to our products, and we always encourage customers to update to the newest software releases to benefit from the latest protections.”
A DMCA notice has been sent to Github to take down the source code.
Machine Learning gone bad
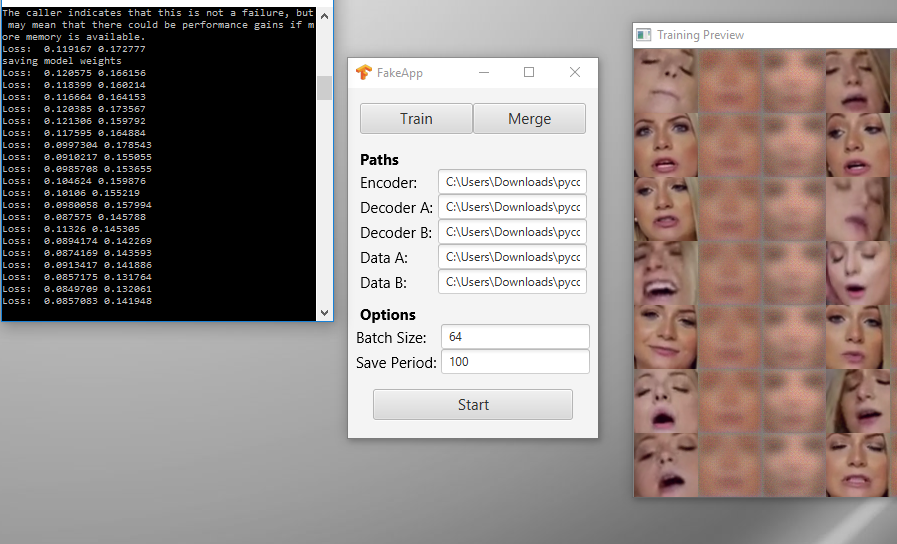
I suppose every new technology will eventually be misused, and this has now come to machine learning and facial recognition algorithms. As reported by Motherboard an app has been launched on reddit using NVIDA’s CUDA framework to morph faces onto another body, to create realistic videos as an outcome. Of course (in an forum dominated by teenage boys) the initial activity is to use celebrity faces in porn scenes, but it raises another worry about trusting digital images and video files in a wider use of this technology.
How much can a Malware payload actually do?
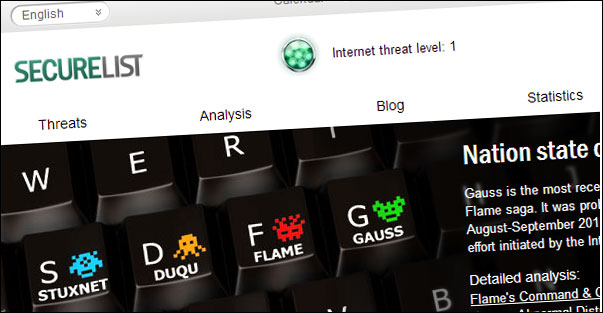
Kapersky has released an advisory on Securelist on a new major Android Malware, originating (it seems) from Italy. Skygofree (as it has been named) goes above and beyond what has been seen before. Skygofree is capable of taking pictures, capturing video, and seizing call records, text messages, gelocation data, calendar events, and business-related information stored in device memory. Skygofree also includes the ability to automatically record conversations and noise when an infected device enters a location specified by the person operating the malware. Also a clever use of Androids Accessibility Service gives backdoor access to Whatsapp. Deeper analysis leads to finding a set of windows components indicating an almost full Windows implementation of the above.
For those looking to validate if they are impacted, here are the indicators.
Uber/Waymo: Jacob’s letter released to the public
The letter written by Richard Jacobs to senior management in Uber (leading to his job demotion and eventually leaving Uber) that delayed the current court case between Waymo (Google) and Uber when discovered. This document has now been (mostly) made public by the court. The complete document can be found on Scripted, some initial analysis can be found on Engadet, CNN and on Verge.
This gives an uncensored and scary insight of how corporate espionage and hacking seems the be a key part of Ubers business model and operations.
A true physical “man in the middle” attack
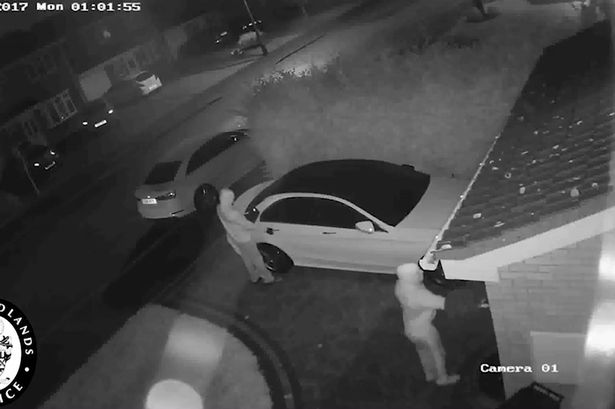
There has been known weaknesses with the various key less entry solutions among cat manufacturers, the debacle on the system used by JEEP springs to mind. Now we see a weakness in the Mercedes Benz solution. In a video released by the West Midlands Police in the UK we see thieves sniffing out the key code from the key inside of the house, and then transfers it to a sender by the car to open and start the car. Time to look at at NFC blocking key storage I suppose.
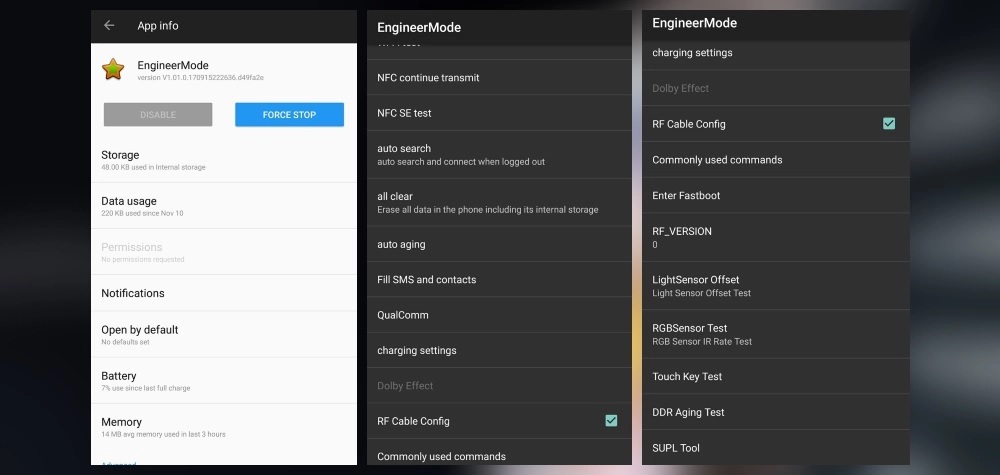
Note to Oneplus: Remember to clean up devices after QA
There has been a lot of discussions on the amount of data transmitted by Oneplus devices to the mother ship. A security researcher suing the monikor Elliot Alderson decided to dig deeper to find out what data was being sent. As he dug through the OS (OxygenOS) on his phone he discovered an EngineerMode app. This app (assumed to be an internal testing tool for QA) gives access to all aspects of the phone, including rooting. A quick check for Oneplus owners it to enter *#808# SSID, which will bring up the app if present. A hcak (for now) requires physical access.
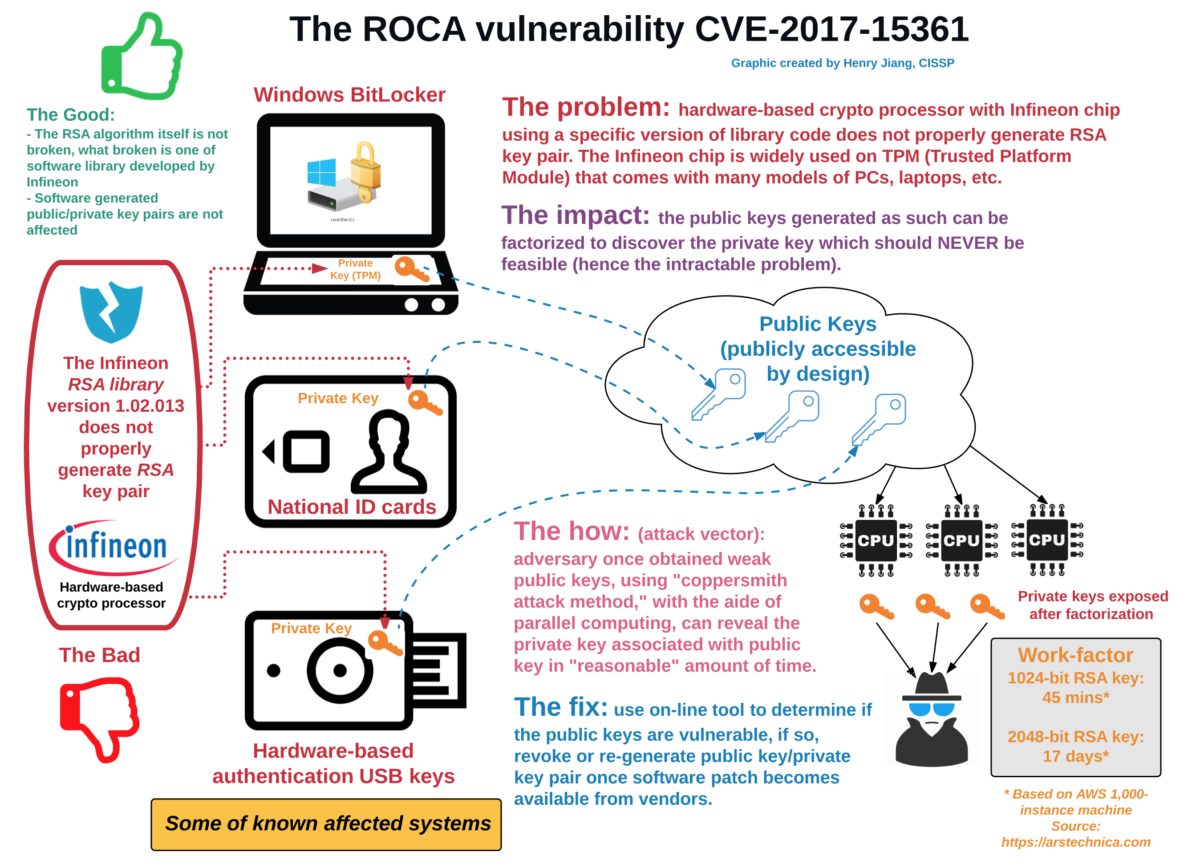
The Return of Coppersmith’s Attack
The Infineon-developed RSA Library version v1.02.013, arguably one the most commonly used libraries for RSA Prime Calculations in almost all major public PKI solutions has been discovered to contain a major flaw in the way the randomness of the keys are calculated. A study by Matus Nemec, Marek Sys, Petr Svenda, Dusan Klinec and Vashek Matyas shows that “…our discovery of an algorithmic aw in the construction of primes for RSA key generation in a widely-used library of a major manufacturer of cryptographic hardware. The primes generated by the library suffer from a signicant loss of entropy”.
This has had massive impacts, perhaps the most public is the cancellation of a major part of the current generation of National ID Cards in Lithuania. Remember that security without randomness is no security!
Another Crypto Currency Hard Fork?
Etherum (the most referred to competitor to Bitcoin currently) has had another “incident”. You may remember the USD 32 million USD hack on Etherum in July and the subsequent (heavily criticized) hard fork to zero out the hack. Now a “mistake” from a developer has locked down wallets worth USD 300 million. The attack relates to a quirk in Etherum’s multisignature wallets, and will most likely require another hard fork to rectify. Again a warning that crypto currencies are still evolving, in most cases at a slower pace than the money thrown at it.
KRACK: Key Reinstallation Attacks
Mathy Vanhoef and Frank Piessens of KU Leuve have discovered a critical flaw in the way WPA2 encryption for all known WiFi implementations. Some time to caveat on the width of the discovery, the attacker needs physical access to the network, and will only see non-encrypted transmissions. Until the vendors patch their implementations the only interim solution is to treat your home WiFi as you would a public WiFi, using HTTPS and in an ideal world VPN form the individual client.
This overview on Github shows the current state of fixes from the vendors. I somewhat sadly note that the majority of my HW is under the “No Known Official Response” category!

![[Updated] More Apple iOS source code leaks (iBoot)](https://www.solberg.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/1518047804451-Screen-Shot-2018-02-07-at-63528-PM.jpg)